


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 308-316.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.03.009
王清玉( ), 林征(
), 林征( ), 雷阳, 周美景, 王咪, 孙彩云, 顾珺怡, 朱展慧, 唐李晨, 卞秋桂
), 雷阳, 周美景, 王咪, 孙彩云, 顾珺怡, 朱展慧, 唐李晨, 卞秋桂
收稿日期:2023-07-21
出版日期:2024-02-10
发布日期:2024-02-02
通讯作者:
林征,E-mail:linzheng100@163.com作者简介:王清玉:女,本科(硕士在读),E-mail:nowtry@stu.njmu.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Qingyu( ), LIN Zheng(
), LIN Zheng( ), LEI Yang, ZHOU Meijing, WANG Mi, SUN Caiyun, GU Junyi, ZHU Zhanhui, TANG Lichen, BIAN Qiugui
), LEI Yang, ZHOU Meijing, WANG Mi, SUN Caiyun, GU Junyi, ZHU Zhanhui, TANG Lichen, BIAN Qiugui
Received:2023-07-21
Online:2024-02-10
Published:2024-02-02
摘要:
目的 探究炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展的潜在剖面类别,并分析不同类别的影响因素。方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2022年7月—2023年7月在南京市某三级甲等医院住院的炎症性肠病患者作为调查对象。使用一般资料调查表、中文版恐惧疾病进展简化量表、中文版炎症性肠病自我效能量表和社会支持评定量表进行调查。对炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展进行潜在剖面分析,并通过单因素分析和多元Logistic回归分析探讨其影响因素。结果 共回收问卷310份,其中有效问卷303份,有效问卷回收率为97.74%。潜在剖面分析结果显示,炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展分为“低恐惧风险-疾病适应组”(n=127,41.91%)、“中恐惧风险-疾病困扰组”(n=139,45.88%)、“高恐惧风险-功能失调组”(n=37,12.21%)3个潜在剖面类别。其影响因素包括居住地、自评经济压力水平、疾病分期、自我效能(P<0.05)。结论 炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展水平具有明显的异质性。护理人员应根据该分类特点制订个性化干预策略,着重提高患者的自我效能,提升其疾病、压力及情绪管理水平。
王清玉, 林征, 雷阳, 周美景, 王咪, 孙彩云, 顾珺怡, 朱展慧, 唐李晨, 卞秋桂. 炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展潜在类别的影响因素分析及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 308-316.
WANG Qingyu, LIN Zheng, LEI Yang, ZHOU Meijing, WANG Mi, SUN Caiyun, GU Junyi, ZHU Zhanhui, TANG Lichen, BIAN Qiugui. Influencing factors and nursing enlightenment of the fear of progression in patients with inflammatory bowel disease:a latent profile analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(3): 308-316.
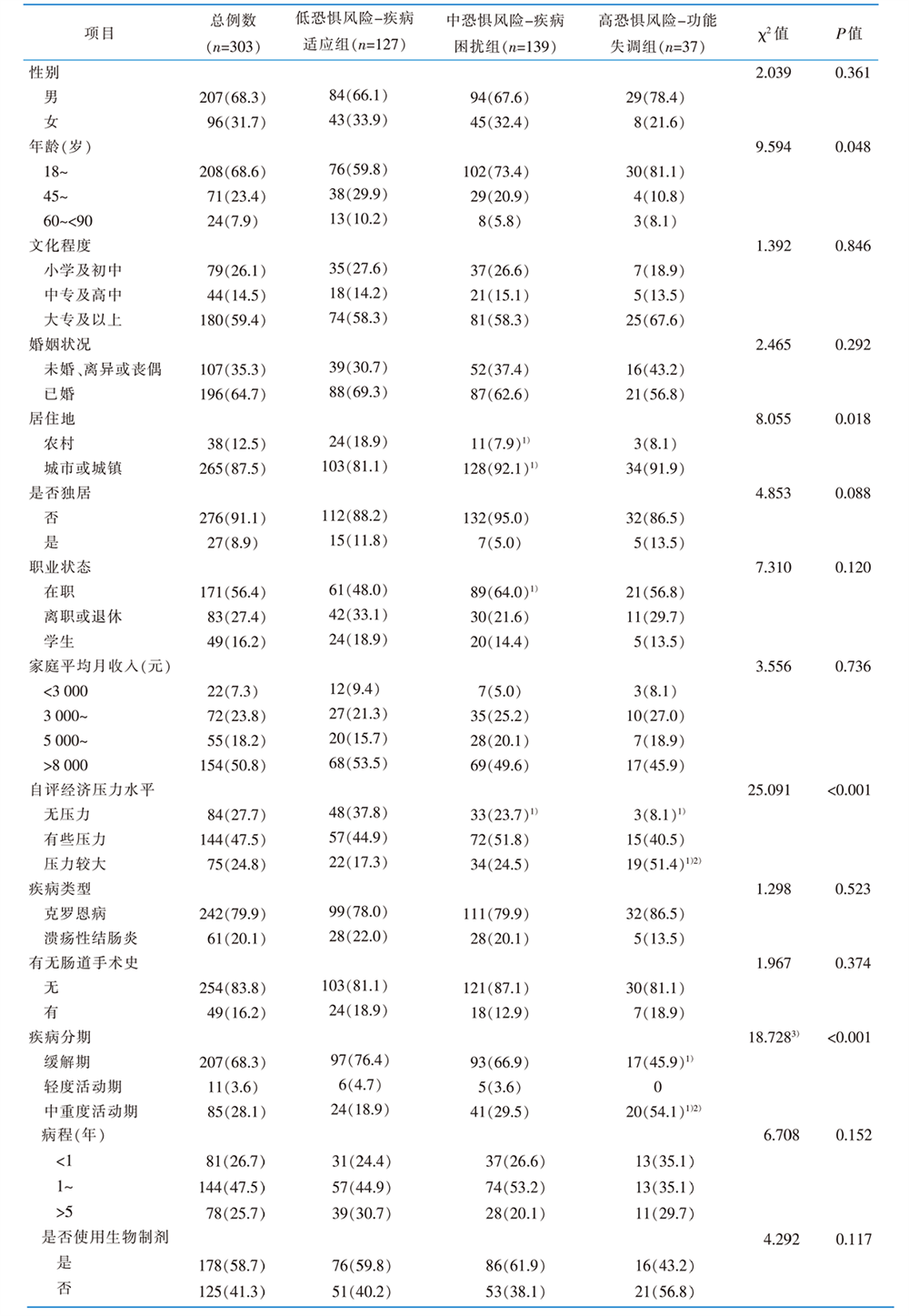 |
表1 炎症性肠病患者的一般资料及恐惧疾病进展潜在类别的单因素分析结果 [例(百分比,%)]
Table 1 General data and univariate analysis of potential categories of fear of progression among inflammatory bowel disease patients [cases(percentages,%)]
 |
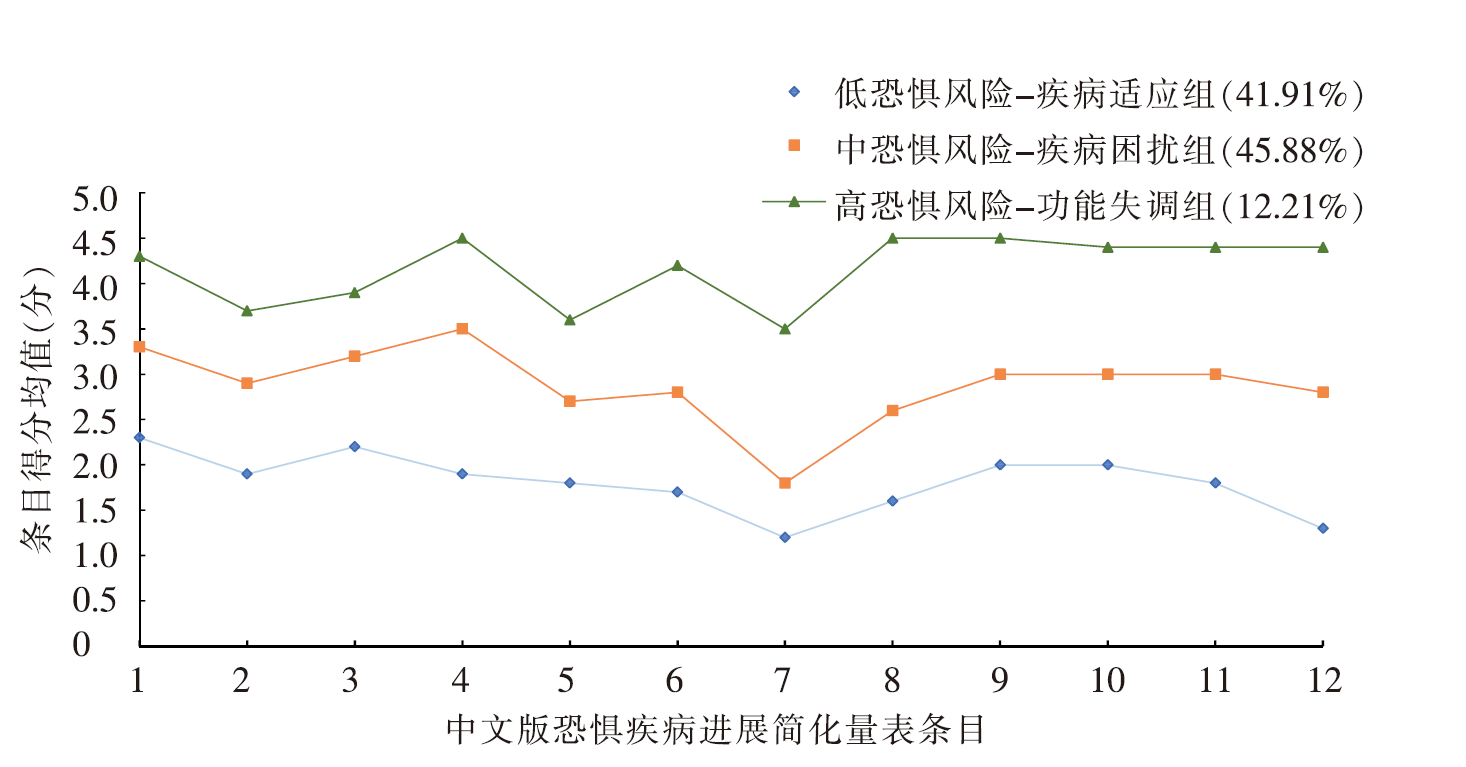
图1 炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展3个潜在类别的特征分布
Figure 1 The characteristic distribution of 3 potential categories of the fear of progression among patients with inflammatory bowel disease
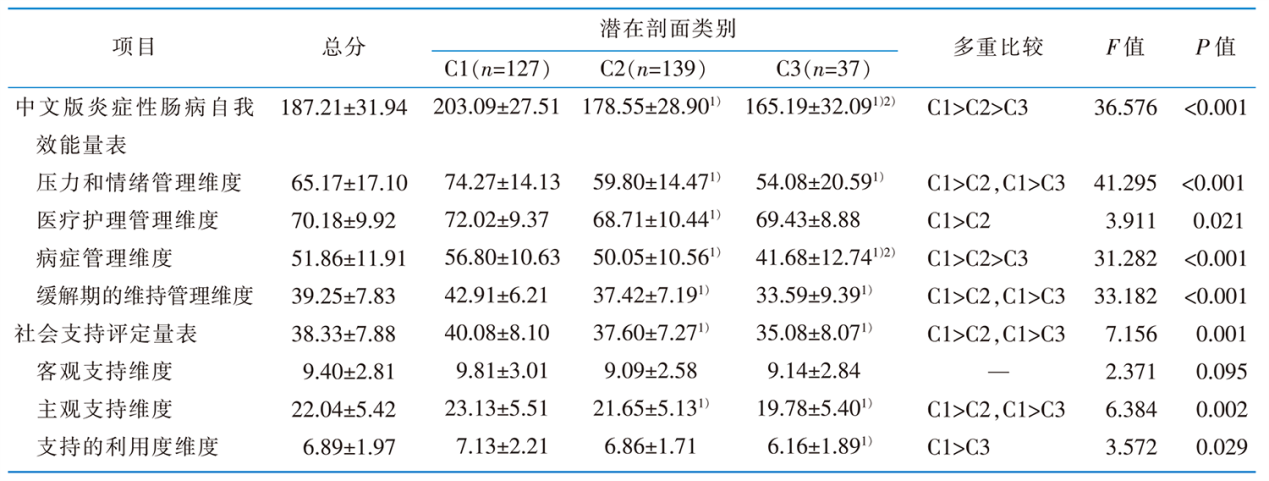 |
表3 炎症性肠病患者的中文版炎症性肠病自我效能量表、社会支持评定量表得分在不同潜在类别间的比较(n=303,分,$ \bar{x} \pm s$)
Table 3 Classification of latent profiles of the scores of the IBD-SES and SSRS(n=303,scores,$ \bar{x} \pm s$)
 |
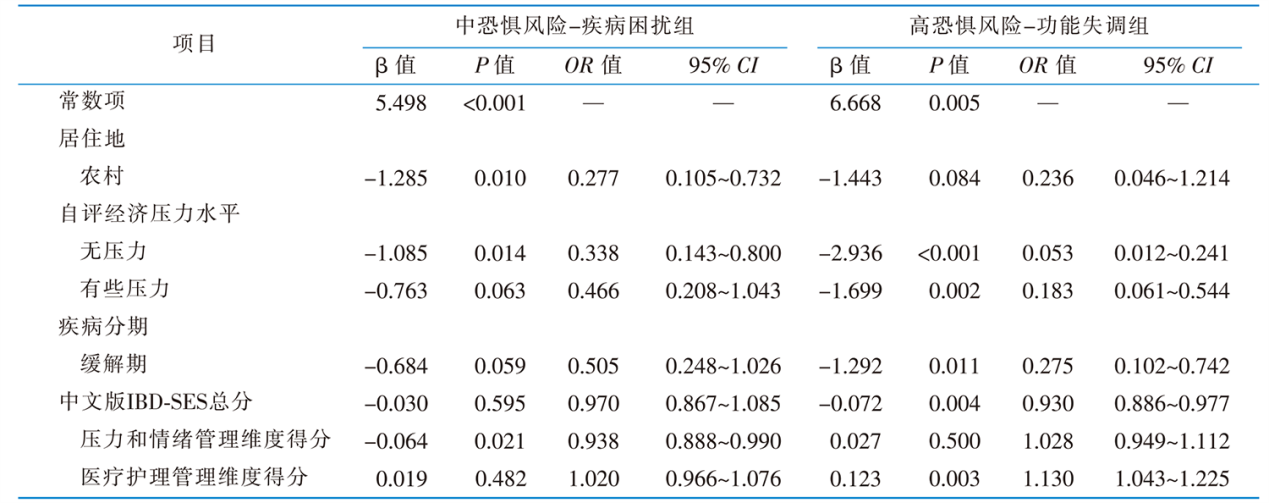 |
表4 炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展潜在类别影响因素的多元Logistic回归分析
Table 4 Multivariate Logistic analysis results on influencing factors of latent profiles of fear of progression in inflammatory bowel disease patients
 |
| [1] |
Agrawal M, Spencer EA, Colombel JF, et al. Approach to the management of recently diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease patients:a user’s guide for adult and pediatric gastroenterologists[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 161(1):47-65.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Shao BL, Yang WJ, Cao Q. Landscape and predictions of inflammatory bowel disease in China:China will enter the compounding prevalence stage around 2030[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10:1032679.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 李建冰. 炎症性肠病复发的临床特征及危险因素分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. |
| Li JB. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of recurrent inflammatory bowel disease[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. | |
| [4] |
Monstad IL, Solberg IC, Cvancarova M, et al. Outcome of ulcerative colitis 20 years after diagnosis in a prospective population-based inception cohort from south-eastern Norway,the IBSEN study[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2021, 15(6):969-979.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Hamilton AL, Kamm MA, De Cruz P, et al. Luminal microbiota related to Crohn’s disease recurrence after surgery[J]. Gut Microbes, 2020, 11(6):1713-1728.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Fourie S, Jackson D, Aveyard H. Living with inflammatory bowel disease:a review of qualitative research studies[J]. Int J Nurs Stud, 2018, 87:149-156.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Yu Q, Zhu CP, Feng SY, et al. Economic burden and health care access for patients with inflammatory bowel diseases in China:web-based survey study[J]. J Med Internet Res, 2021, 23(1):e20629. |
| [8] |
Keller R, Mazurak N, Fantasia L, et al. Quality of life in inflammatory bowel diseases:it is not all about the bowel[J]. Intest Res, 2021, 19(1):45-52.
DOI URL |
| [9] | 孟婷, 薛鲜敏, 樊晓辉, 等. 炎症性肠病患者恐惧疾病进展现状和生活质量分析[J]. 胃肠病学, 2021, 26(4):198-203. |
| Meng T, Xue XM, Fan XH, et al. Analysis of fear of progression and quality of life in patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Chin J Gastroenter, 2021, 26(4):198-203. | |
| [10] |
Dankert A, Duran G, Engst-Hastreiter U, et al. Fear of progression in patients with cancer,diabetes mellitus and chronic arthritis[J]. Die Rehabil, 2003, 42(3):155-163.
DOI URL |
| [11] | 顾雨亭, 赵梦佳, 舒成园, 等. 脑卒中半失能老年患者自我效能与复发恐惧之间的关联:不同社会支持类型的中介作用[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2023, 31(8):1161-1166. |
| Gu YT, Zhao MJ, Shu CY, et al. Association between self-efficacy and fear of recurrence in semi-disabled elderly patients with stroke:the mediating role of different types of social support[J]. China J Health Psychol, 2023, 31(8):1161-1166. | |
| [12] |
尹奎, 彭坚, 张君. 潜在剖面分析在组织行为领域中的应用[J]. 心理科学进展, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI |
|
Yin K, Peng J, Zhang J. The application of latent profile analysis in organizational behavior research[J]. Adv Psychol Sci, 2020, 28(7):1056-1070.
DOI |
|
| [13] |
中华医学会消化病学分会炎症性肠病学组. 炎症性肠病诊断与治疗的共识意见(2018年·北京)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(9):796-813.
DOI |
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese consensus on diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease(Beijing,2018)[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2018, 38(9):796-813. | |
| [14] | 倪平, 陈京立, 刘娜. 护理研究中量性研究的样本量估计[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2010, 45(4):378-380. |
| Ni P, Chen JL, Liu N. The sample size estimation of quantitative nursing research[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2010, 45(4):378-380. | |
| [15] |
Walmsley RS, Ayres RCS, Pounder RE, et al. A simple clinical colitis activity index[J]. Gut, 1998, 43(1):29-32.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Truelove SC, Witts LJ. Cortisone in ulcerative colitis:final report on a therapeutic trial[J]. Br Med J, 1955, 2(4947):1041-1048. |
| [17] |
Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM. A simple index of Crohn’s-disease activity[J]. Lancet, 1980, 1(8167):514.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Mehnert A, Herschbach P, Berg P, et al. Fear of progression in breast cancer patients:validation of the short form of the Fear of Progression Questionnaire(FoP-Q-SF)[J]. Z Psychosom Med Psychother, 2006, 52(3):274-288.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | 吴奇云, 叶志霞, 李丽, 等. 癌症患者恐惧疾病进展简化量表的汉化及信效度分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015, 50(12):1515-1519. |
| Wu QY, Ye ZX, Li L, et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of Fear of Progression Questionnaire-Short Form for cancer patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2015, 50(12):1515-1519. | |
| [20] |
Keefer L, Kiebles JL, Taft TH. The role of self-efficacy in inflammatory bowel disease management:preliminary validation of a disease-specific measure[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2011, 17(2):614-620.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 徒文静, 徐桂华. 中文版炎性肠病自我效能量表的信效度研究[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2014, 30(22):18-21. |
| Tu WJ, Xu GH. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Self-Efficacy Scale[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2014, 30(22):18-21. | |
| [22] | 肖水源. 《社会支持评定量表》的理论基础与研究应用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志, 1994, 4(2):98-100. |
| Xiao SY. Theoretical basis and research application of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Clin Psychol Med, 1994, 4(2):98-100. | |
| [23] | 刘继文, 李富业, 连玉龙. 社会支持评定量表的信度效度研究[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2008, 31(1):1-3. |
| Liu JW, Li FY, Lian YL. Investigation of reliability and validity of the Social Support Scale[J]. J Xinjiang Med Univ, 2008, 31(1):1-3. | |
| [24] |
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Lee JY, et al. Common method biases in behavioral research:a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies[J]. J Appl Psychol, 2003, 88(5):879-903.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Preacher KJ, Merkle EC. The problem of model selection uncertainty in structural equation modeling[J]. Psychol Methods, 2012, 17(1):1-14.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | 国家医疗保障局. 国家医保局人力资源社会保障部关于印发《国家基本医疗保险、工伤保险和生育保险药品目录(2021年)》的通知[EB/OL]. (2021-12-03)[2023-07-15]. http://www.nhsa.gov.cn/art/2021/12/3/art_37_7429.html. |
| National Healthcare Security Administration. Notice of the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of the National Medical Insurance Administration on the issuance of the drug catalogue of national basic medical insurance,work-related injury insurance and maternity insurance(2021)[EB/OL]. (2021-12-03)[2023-07-15]. http://www.nhsa.gov.cn/art/2021/12/3/art_37_7429.html. | |
| [27] | 国家医疗保障局. 国家医保局财政部国家税务总局关于做好2022年城乡居民基本医疗保障工作的通知[EB/OL]. (2022-07-08)[2023-07-15]. http://www.nhsa.gov.cn/art/2022/7/8/art_104_8398.html. |
| National Healthcare Sec urity Administration. Notice of the state administration of taxation of the Ministry of Finance on to do a good job of 2022 basic medical in-surance for urban and rural residents[EB/OL]. (2022-07-08)[2023-07-15]. http://www.nhsa.gov.cn/art/2022/7/8/art_104_8398.html. | |
| [28] |
赵继明, 房晓, 孟俏, 等. 肾移植患者个人生活掌控感现状及其影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(10):1213-1218.
DOI |
|
Zhao JM, Fang X, Meng Q, et al. Status and influencing factors of personal mastery in kidney transplant patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(10):1213-1218.
DOI |
|
| [29] | 张杰兰, 赖先婷, 余兆兰, 等. 维持性血液透析患者配偶恐惧疾病进展的现状及影响因素分析[J]. 护理学报, 2022, 29(7):17-22. |
| Zhang JL, Lai XT, Yu ZL, et al. Status of fear of progression in spouses of maintenance hemodialysis patientsand its influencing factors[J]. J Nurs, 2022, 29(7):17-22. | |
| [30] |
马丽, 杨小珍, 南锐伶, 等. 癌症患儿父母恐惧疾病进展的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(18):2282-2287.
DOI |
|
Ma L, Yang XZ, Nan RL, et al. Research progress on fear of progression among parents of children with cancer[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(18):2282-2287.
DOI |
| [1] | 胡雁, 荆凤. 护理领域混合方法研究的设计要点及典型问题分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 261-266. |
| [2] | 王志稳, 韩舒羽. 护理领域专家共识论文的质量评价要点[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 267-270. |
| [3] | 胡荣, 王春凤. 随机对照研究护理论文的撰写要点及常见问题分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 271-275. |
| [4] | 刘均娥, 王莹, 孙柳. 质性研究护理论文的撰写与质量评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 276-280. |
| [5] | 范蕾, 宋继红, 陈少华, 杨辛茹, 赵亚曼, 吴杰灵. 护理领域系统评价的报告要素与问题分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 281-286. |
| [6] | 王克芳, 徐东娟, 王雅琦. 护理领域量表类论文问题分析及建议[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 287-291. |
| [7] | 吴前胜, 曾莹, 王兰, 王萧萧, 周雁荣. 体外循环下心脏手术患者术后谵妄管理的循证实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 292-299. |
| [8] | 胡哲, 雷丹丹, 赵益, 杨阳, 高月. 基于健康行为改变整合理论的护理干预对糖尿病视网膜病变患者的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 300-307. |
| [9] | 付荣娟, 丁福. 临床跌倒防范信息系统的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 317-323. |
| [10] | 张丰健, 张海鑫, 刘义兰, 潘绍山, 郭舒婕, 辛霞, 杨艳, 奚慧琴, 李秀娥, 程远娟, 莫蓓蓉, 黎蔚华, 张小红, 王芳, 王红霞. 30个省份医院患者对护理人文关怀感知的现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 324-329. |
| [11] | 李亚敏, 李栩亭, 余强, 杨佳欣, 陈亚敏, 陈曾煜, 宁檬, 李斯妮, 田于胜, 吴欣娟. 护士健康队列研究的大样本文献计量学分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 330-337. |
| [12] | 吴白女, 米元元, 郑义, 张柳柳, 章毛毛, 邾萍, 刘春丽, 吴冰, 羌燕. 食管癌术后患者肠内营养相关性腹泻管理流程的制订与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 338-344. |
| [13] | 梁江淑渊, 曾妃, 兰美娟, 顾培培, 蔡凌云, 郭璐瑶, 朱岩, 郭鸽. 体外膜肺氧合清醒患者早期活动的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 345-352. |
| [14] | 张若萱, 赵健, 牟利宁. 钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制剂导致酮症酸中毒的Meta分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 353-361. |
| [15] | 冯琦凡, 涂发妹, 吴季敏, 刘萍萍, 刘佳晨, 张思易, 张鑫. 烧伤患者身体意象体验质性研究的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(3): 362-370. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||