


中华护理杂志 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (8): 922-929.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.08.004
尤朝香( ), 贾梦滢, 李霜, 陈莉莉, 敬文丹, 寇红艳(
), 贾梦滢, 李霜, 陈莉莉, 敬文丹, 寇红艳( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-04
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-04-22
通讯作者:
寇红艳,E-mail:546288545@qq.com作者简介:尤朝香: 女,硕士,护师,E-mail:287731927@qq.com
YOU Chaoxiang( ), JIA Mengying, LI Shuang, CHEN Lili, JING Wendan, KOU Hongyan(
), JIA Mengying, LI Shuang, CHEN Lili, JING Wendan, KOU Hongyan( )
)
Received:2023-05-04
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-04-22
摘要:
目的 探讨直肠癌患者经腹腔镜保肛术后6个月内症状群纵向轨迹,并分析各轨迹的影响因素。 方法 采用纵向研究设计,便利选取2021年11月-2022年4月于南充市某三级甲等综合医院胃肠外科行经腹腔镜保肛术的128例直肠癌患者作为调查对象。使用一般资料调查表、中文版安德森消化道癌症状评估量表及查尔森合并症指数于患者术后2周、1个月、3个月、6个月进行4次调查。采用探索性因子分析提取症状群,构建潜类别增长模型识别各症状群轨迹亚组,使用Mplus软件纳入预测变量,分析各轨迹的影响因素。 结果 探索性因子分析结果显示,直肠癌患者经腹腔镜保肛术后6个月内存在4组症状群,分别命名为病感症状群、心理-睡眠症状群、胃肠道症状群、心理-治疗相关症状群,方差贡献率分别为65.173%、66.225%、62.421%、60.492%。潜类别增长模型识别出症状群存在4~5个轨迹,女性患者、文化程度低、查尔森合并症指数高、原发肿瘤分期高、医疗费用负担重、治疗方式为化疗+手术是症状群高危轨迹的预测因素(P<0.05)。 结论 直肠癌患者经腹腔镜保肛术后6个月内存在4组症状群,胃肠道症状群是此类患者的特异性症状群,症状负担最重。各症状群轨迹总体呈动态缓解趋势,但个别轨迹亚组仍有加重趋势。不同症状群的影响因素存在差异,临床医护人员应及时识别高危人群,动态调整相应的干预方针,提高精准护理质量。
尤朝香, 贾梦滢, 李霜, 陈莉莉, 敬文丹, 寇红艳. 直肠癌患者经腹腔镜保肛术后的症状群轨迹及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 922-929.
YOU Chaoxiang, JIA Mengying, LI Shuang, CHEN Lili, JING Wendan, KOU Hongyan. A study of longitudinal trajectories and predictive factors of symptom clusters in patients with laparoscopic anal preservation surgery for rectal cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2024, 59(8): 922-929.
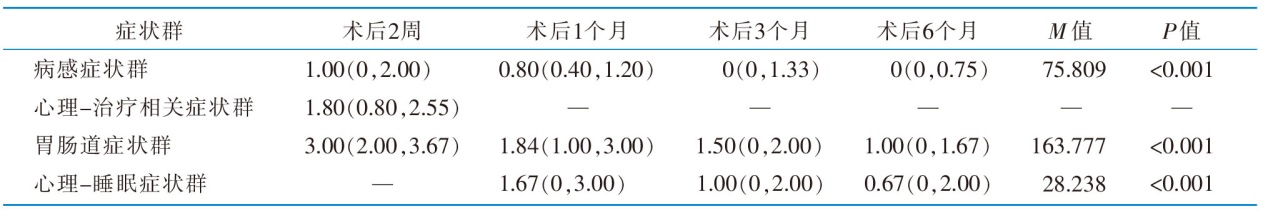 |
表3 直肠癌患者经腹腔镜保肛术后症状群严重程度得分[n=128,分,M(P25,P75)]
Table 3 Symptom clusters severity score of rectal cancer after laparoscopic anal preservation surgery[n=128,scores,M(P25,P75)]
 |
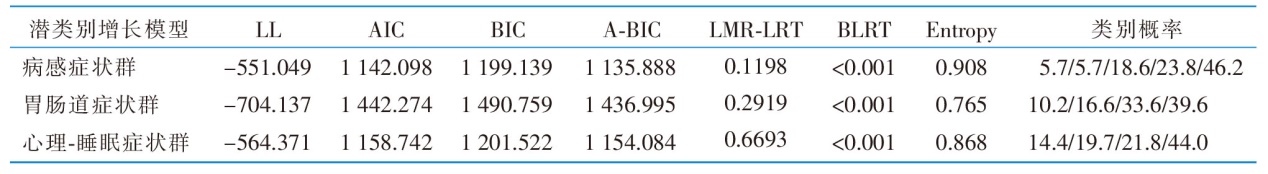 |
表4 直肠癌患者经腹腔镜保肛术后各症状群潜类别增长模型拟合指标
Table 4 Symptom cluster fitting index in LCGM model of rectal cancer within six months after laparoscopic anal preservation surgery
 |
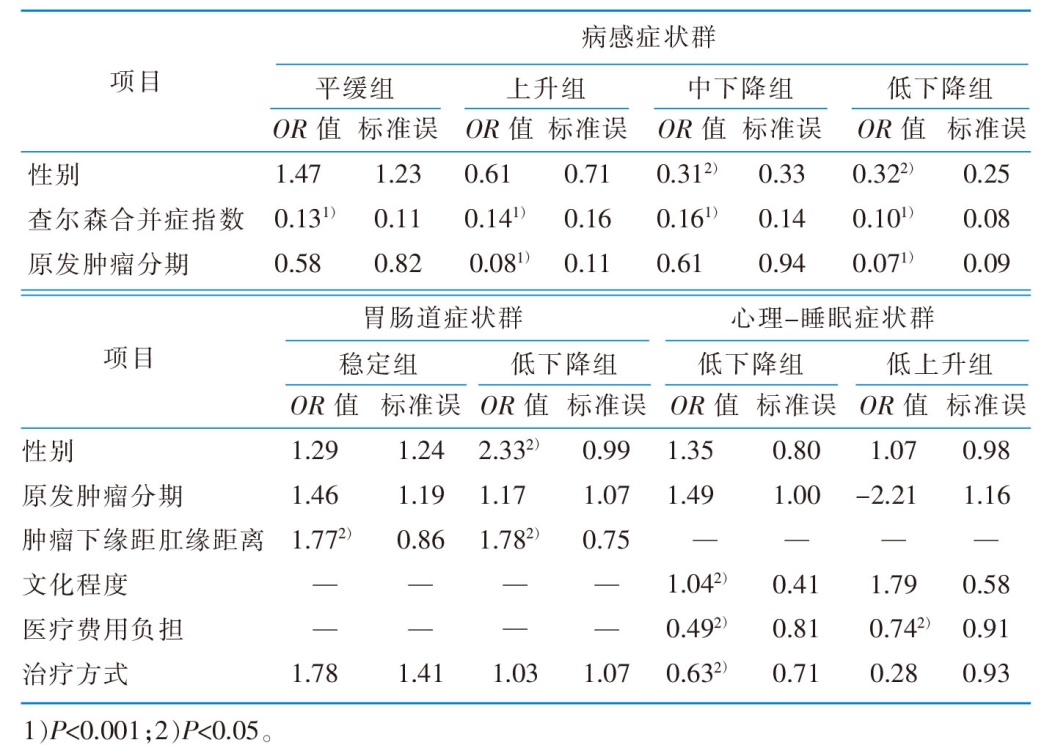 |
表6 直肠癌患者经腹腔镜保肛术后各症状群轨迹类别的预测因素分析结果(n=128)
Table 6 Analysis results of predictive factors of symptom cluster trajectory category in rectal cancer after laparoscopic anal preservation surgery(n=128)
 |
| [1] |
Xi Y, Xu P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040[J]. Transl Oncol, 2021, 14(10):101174.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 葛思堂, 邱权威, 郝博, 等. 腹腔镜辅助经肛全直肠系膜切除术在低位直肠癌保肛根治术中的应用研究[J]. 中华解剖与临床杂志, 2022, 27(2):92-97. |
| Ge ST, Qiu QW, Hao B, et al. Application of laparoscopically assisted transanal total mesorectal excision in the anal-preserving radical resection of low rectal cancer[J]. Chin J Anat Clin, 2022, 27(2):92-97. | |
| [3] | 侯森, 叶颖江. 不同保肛术式对低位直肠癌术后排粪功能的影响[J]. 中华胃肠外科杂志, 2022, 25(6):482-486. |
| Hou S, Ye YJ. Influence of different sphincter-preserving surgeries on postoperative defecation function[J]. Chin J Gastrointest Surg, 2022, 25(6):482-486. | |
| [4] | 解秀娟, 关红, 涂舒涵, 等. 慢性病患者症状群管理的研究进展[J]. 中国护理管理, 2022, 22(8):1266-1270. |
| Xie XJ, Guan H, Tu SH, et al. Research progress on the management of symptom clusters of patients with chronic diseases[J]. Chin Nurs Manag, 2022, 22(8):1266-1270. | |
| [5] | 任仕泉, 陈峰, 杨树勤. 重复采样试验设计的样本含量估计[J]. 中国卫生统计, 1999, 16(4):194-196. |
| Ren SC, Chen F, Yang SQ. Sample size estimation of hypothesis testing for repeated sampling[J]. Chin J Health Statistics, 1999, 16(4):194-196. | |
| [6] | 罗宝嘉, 阳霞, 陈春燕, 等. 中低位直肠癌保肛术后患者排便功能与生活质量的现状及相关性研究[J]. 护士进修杂志, 2021, 36(24):2209-2213. |
| Luo BJ, Yang X, Chen CY, et al. Study for the correlation between defecation function and quality of life among low and middle rectal cancer patients with sphincter-saving resection[J]. J Nurses Train, 2021, 36(24):2209-2213. | |
| [7] | 冯芳茗, 张伟英, 何佳倩, 等. 消化道癌症患者化疗期间症状群及影响因素分析[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2020, 37(9):13-17. |
| Feng FM, Zhang WY, He JQ, et al. Symptom clusters and influencing factors for patients with gastrointestinal cancer during chemotherapy[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2020, 37(9):13-17. | |
| [8] | 李桂, 聂小菲, 陈晓莉, 等. 结直肠癌患者术后化疗期间的症状群研究[J]. 护理学杂志, 2017, 32(22):15-19. |
| Li G, Nie XF, Chen XL, et al. Symptom cluster in surgically treated colorectal cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2017, 32(22):15-19. | |
| [9] |
Wang XS, Wang Y, Guo H, et al. Chinese version of the M. D. Anderson Symptom Inventory:validation and application of symp-tom measurement in cancer patients[J]. Cancer, 2004, 101(8):1890-1901.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 毕岑, 景丽伟, 邹圣强, 等. 食管癌病人术后早期症状群与生活质量的相关性研究[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(20):3614-3618. |
| Bi C, Jing LW, Zou SQ, et al. Correlation between postoperative early symptom clusters and quality of life in patients with esophageal cancer[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(20):3614-3618. | |
| [11] |
Charlson ME, Carrozzino D, Guidi J, et al. Charlson Comorbidity Index:a critical review of clinimetric properties[J]. Psychother Psychosom, 2022, 91(1):8-35.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | 国家卫生健康委员会, 中华医学会肿瘤学分会. 中国结直肠癌诊疗规范(2023年版)[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2023, 61(8):617-644. |
| National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, Chinese Society of Oncology. Chinese protocol of diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer(2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Surg, 2023, 61(8):617-644. | |
| [13] |
文翠菊, 王玥妮, 孙红娟, 等. 芳香化酶抑制剂治疗期间乳腺癌患者症状群对生活质量的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(8):1201-1207.
DOI URL |
|
Wen CJ, Wang YN, Sun HJ, et al. Symptom clusters and the effects on quality of life among breast cancer patients receiving aromatase inhibitors[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(8):1201-1207.
DOI URL |
|
| [14] | 江晓蕾, 邹天韵. 恶性血液病患者心理症状群及其影响因素[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2019, 39(9):1983-1988. |
| Jiang XL, Zou TY. Mental symptom group and its influencing factors in patients with hematological malignancy[J]. J Clin Pathol Res, 2019, 39(9):1983-1988. | |
| [15] | 胡丰阳. Ⅱ-Ⅲ期直肠癌术前放化疗患者症状群及其生活质量的调查研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2018. |
| Hu FY. Investigation on symptoms and quality of life in patients with stage Ⅱ-Ⅲ rectal cancer undergoing preoperative chemoradiotherapy[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2018. | |
| [16] | 文翠菊, 王玥妮, 孙红娟, 等. 乳腺癌患者芳香化酶抑制剂治疗期间症状群及影响因素分析[J]. 中国实用护理杂志, 2022, 38(2):132-139. |
| Wen CJ, Wang YN, Sun HJ, et al. Analysis on the symptom clusters and influencing factors among breast cancer patients during aromatase inhibitors treatment[J]. Chin J Pract Nurs, 2022, 38(2):132-139. | |
| [17] | 易彩云. 结直肠癌患者症状群非药物干预研究进展[J]. 实用癌症杂志, 2021, 36(10):1737-1740. |
| Yi CY. Research progress of the non-pharmacological interventions for colorectal cancer patients’ symptom clusters[J]. Pract J Cancer, 2021, 36(10):1737-1740. | |
| [18] | 伊若男, 刘伟伟, 刘红霞, 等. 结直肠癌术后患者无法忍受不确定性对心理痛苦影响的作用路径分析[J]. 护理学杂志, 2023, 38(17):95-99. |
| Yi RN, Liu WW, Liu HX, et al. Effect of intolerance of uncertainty on cancer-related distress in patients with colorectal cancer after operation:a path analysis[J]. J Nurs Sci, 2023, 38(17):95-99. | |
| [19] | 庞雪滢, 胡少华, 王婷. 直肠癌保肛术后低位前切除综合征评估工具及护理干预措施的研究进展[J]. 解放军护理杂志, 2020, 37(5):82-85. |
| Pang XY, Hu SH, Wang T. Research progress on assessment tools and nursing interventions for low anterior resection syndrome after anus-preserving surgery for rectal cancer[J]. Nurs J Chin PLA, 2020, 37(5):82-85. | |
| [20] |
吴傅蕾, 袁长蓉, 杨瑒, 等. 乳腺癌患者化疗期症状群困扰风险预测模型的构建与评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(6):676-682.
DOI URL |
|
Wu FL, Yuan CR, Yang Y, et al. Development and evaluation of a risk predictive model for high level of self-reported symptom cluster distress in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(6):676-682.
DOI URL |
|
| [21] |
杨俊琳, 杨健, 赵丽丽, 等. 大肠癌放化疗患者消化道症状群护理的证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(1):98-104.
DOI URL |
|
Yang JL, Yang J, Zhao LL, et al. Evidence summary for the nursing of gastrointestinal symptom clusters in colorectal cancer patients with chemoradiotherapy[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2023, 58(1):98-104.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 余良梦, 俞小玲, 李佳镁, 阮晓芬. 证据图谱在护理学领域的应用进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 1021-1025. |
| [2] | 郭苗苗, 严婷婷, 许丹丹, 袁玲. 乳腺癌患者全病程管理信息系统的开发与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 901-908. |
| [3] | 乔文博, 侯思佳, 朱柯平, 李雅琴, 吴思远, 祁子怡, 王薇. 前列腺癌根治术患者盆底肌训练方案的构建及初步应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 909-915. |
| [4] | 路平, 王晓杰, 郭海凌. 老年乳腺癌患者术前衰弱与术后短期并发症的相关性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 916-921. |
| [5] | 毛云涛, 陈丽莉, 陈笑笑, 王莺. 1例机器人辅助切除巨大肾细胞癌伴Ⅲ级癌栓患者的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 930-933. |
| [6] | 高超越, 李敏, 张银珠, 张培莉, 侯晓雅, 程伊霞. 肿瘤术后辅助化疗患者特殊用途配方食品营养管理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 934-940. |
| [7] | 房钰, 郝媛媛, 张晨, 董莹, 吴赢鑫, 姜桂春. 癌症患者决策疲劳的研究进展及护理启示[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 941-946. |
| [8] | 王龙君, 王丹, 徐海莉, 金歌, 方艳艳, 曾庆虎. 积木拼插游戏在学龄期PICC置管患儿上肢功能锻炼中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 947-952. |
| [9] | 侯佳雨, 杨丽, 李佳, 吕润田. 首发脑卒中患者创伤后应激障碍症状的网络分析及护理对策[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 953-959. |
| [10] | 赵鑫淼, 单思雨, 白茹雪, 程逸帆, 夏春玲. 双胎孕产妇健康教育与心理社会需求的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 960-966. |
| [11] | 李卫涛, 王金艳, 吴慧玲, 张菲, 杨长捷, 吴丽萍. 胎儿异常引产产妇创伤后成长历程的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 967-973. |
| [12] | 宋晓安, 卢兴泉, 马静, 王亚凡, 王晓华, 任红, 高俊. 新入职护士考核评估管理信息系统的开发与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 974-979. |
| [13] | 姚斌莲, 徐敏, 叶梦华, 陈晓洁, 叶富英, 汪永坚, 林娟英, 倪斐琳, 张晓兰. 浙江省“互联网+中医护理服务”人才培养模式的构建与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 980-986. |
| [14] | 郭凡, 王敏, 顾肖, 周英凤, 蒋玲, 黄琴, 程念开, 陈怡雷. 俯卧位通气患者眼部并发症护理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 987-995. |
| [15] | 陶伏莹, 石秦川, 张盼盼, 蔡如意, 徐倩, 蒋佳男, 付东英, 黄晓燕, 田莹莹. NICU患儿外周静脉输液外渗预防与处理的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2024, 59(8): 996-1004. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||