


中华护理杂志 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 406-413.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2023.04.003
收稿日期:2022-08-12
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2023-02-21
通讯作者:
杨巧红,E-mail:yqiaohong@163.com作者简介:苏瑾:女,本科(硕士在读),护师,E-mail:aaaaaahon@126.com
基金资助:
SU Jin( ), YANG Qiaohong(
), YANG Qiaohong( ), LI Yaoxia, XIONG Jiaming, QIU Weiyu
), LI Yaoxia, XIONG Jiaming, QIU Weiyu
Received:2022-08-12
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2023-02-21
摘要:
目的 分析院外早期康复阶段中青年急性心肌梗死(acute myocardial infarction,AMI)患者恐惧疾病进展的现况及其潜在剖面类别,并探讨不同类别的影响因素。 方法 采用便利抽样法,选取2021年1月—2022年8月在广州市某所三级甲等医院住院治疗的中青年AMI患者作为调查对象,采用一般资料调查表、中文版恐惧疾病进展简化量表、中文版压力知觉量表和社会支持评定量表在患者出院后1个月进行调查。对中青年AMI患者恐惧疾病进展进行潜在剖面分析,并通过单因素分析和多元Logistic回归探讨其影响因素。 结果 共纳入调查对象352例,其中文版恐惧疾病进展简化量表得分为44(28,51)分。中青年AMI患者恐惧疾病进展可分为“恐惧低风险型”(23.86%)、“恐惧高风险型”(20.46%)、“严重恐惧型”(55.68%)3个潜在剖面类别,其影响因素包括紧张感、失控感、客观支持、社会支持利用度、慢性合并症情况(均P<0.05)。 结论 中青年AMI患者院外早期康复阶段的恐惧疾病进展水平偏高,且存在异质性。护士应重点关注恐惧高风险型及严重恐惧型患者,并根据不同类别的特征及影响因素,尽早对AMI患者的恐惧疾病进展采取针对性预防及心理护理。
苏瑾, 杨巧红, 李耀霞, 熊佳铭, 邱玮瑜. 中青年急性心肌梗死患者早期康复阶段恐惧疾病进展分型及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 406-413.
SU Jin, YANG Qiaohong, LI Yaoxia, XIONG Jiaming, QIU Weiyu. Classification and influencing factors of fear of progression in young and middle-aged patients with acute myocardial infarction in early rehabilitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2023, 58(4): 406-413.
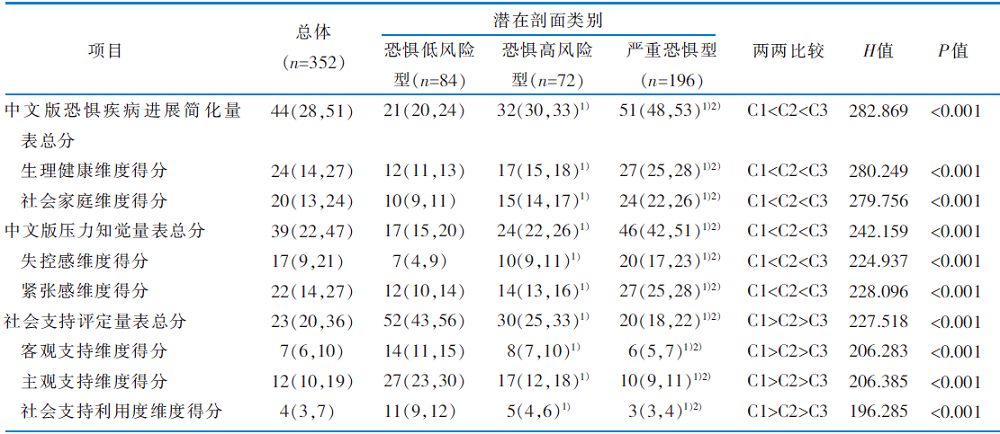 |
表4 调查对象汉化版恐惧疾病进展简化量表、中文版压力知觉量表、社会支持评定量表得分在不同潜在剖面类别间的比较[n=352,分,M(P25,P75)]
Table 4 Classification of latent profiles of the scores of the Fop-Q-SF and PSS, and SSRS[n=352,scores,M(P25,P75)]
 |
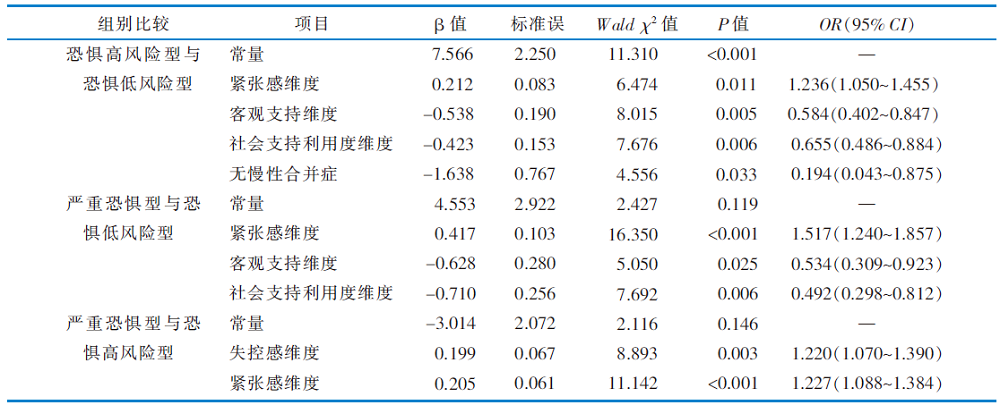 |
表5 中青年急性心肌梗死患者恐惧疾病进展潜在剖面类别的多元Logistic回归结果
Table 5 Multivariate Logistic analysis results on influencing factors of latent profiles of fear of progression in young and middle-aged AMI patients
 |
| [1] |
Song J, Murugiah K, Hu S, et al. Incidence,predictors,and prognostic impact of recurrent acute myocardial infarction in China[J]. Heart, 2021, 107(4):313-318.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 中华护理学会老年护理专业委员会, 中国康复医学会心血管疾病预防与康复专业委员会, 中国老年保健协会脏器康复专业委员会. 心脏康复护理专家共识[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(16):1937-1941. |
| Geriatric Nursing Committee of Chinese Nursing Association, Committee of Cardiac Rehabilitation and Prevention of Chinese Association of Rehabilitation Medicine, Organ Rehabilitation Committee of Chinese Elder Health Care Association. Chinese expert consensus on cardiac rehabilitation nursing care[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(16):1937-1941. | |
| [3] | 袁丽霞, 丁荣晶. 中国心脏康复与二级预防指南解读[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2019, 34(S1):86-90. |
| Yuan LX, Ding RJ. Interpretation of guidelines for cardiac rehabilitation and secondary prevention in China[J]. Chin Circ J, 2019, 34(S1):86-90. | |
| [4] |
Campkin LM, Boyd JM, Campbell DJT. Coronary artery disease patient perspectives on exercise participation[J]. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev, 2017, 37(5):305-314.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Dankert A, Duran G, Engst-Hastreiter U, et al. Fear of progression in patients with cancer,diabetes mellitus and chronic arthritis[J]. Rehabilitation(Stuttg), 2003, 42(3):155-163. |
| [6] |
Fait K, Vilchinsky N, Dekel R, et al. Cardiac-disease-induced PTSD and fear of illness progression:capturing the unique nature of disease-related PTSD[J]. Gen Hosp Psychiatry, 2018, 53:131-138.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Dinkel A, Herschbach P. Fear of progression in cancer patients and survivors[J]. Recent Results Cancer Res, 2018, 210:13-33. |
| [8] | 胡桂丽, 杨艳艳, 徐丹丹, 等. 中青年急性心肌梗死患者疾病进展恐惧现状调查及影响因素分析[J]. 当代护士(上旬刊), 2021, 28(9):9-13. |
| Hu GL, Yang YY, Xu DD, et al. Investigation and influencing factors of fear of progression in young and middle-aged patients with acute myocardial infarction[J]. Mod Nurse, 2021, 28(9):9-13. | |
| [9] | 曾凯, 陈小芳, 屠燕, 等. 急性心肌梗死病人疾病进展恐惧与创伤后应激障碍症状的相关性分析[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(3):380-383. |
| Zeng K, Chen XF, Tu Y, et al. Correlation between fear of disease progress and post-traumatic stress disorder among patients with acute myocardial infarction[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2020, 34(3):380-383. | |
| [10] |
林韦彤, 刘立芳, 万晶晶, 等. 肾移植受者恐惧疾病进展现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1):73-78.
DOI |
|
Lin WT, Liu LF, Wan JJ, et al. The status and factors associated with fear of progression in recipients of renal transplantation[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2022, 57(1):73-78.
DOI |
|
| [11] | 王孟成, 毕向阳. 潜变量建模与Mplus应用-进阶篇[M]. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 2018:13-15. |
| Wang MC, Bi XY. Latent variable modeling and Mplus application-advanced chapter[M]. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press, 2018:13-15. | |
| [12] | 严广斌. NRS疼痛数字评价量表numerical rating scale[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014, 8(3):410. |
| Yan GB. Nr pain numerical rating scale[J]. Chin J Jt Surg Electron Ed, 2014, 8(3):410. | |
| [13] | Mehnert A, Herschbach P, Berg P, et al. Fear of progression in breast cancer patients:validation of the short form of the Fear of Progression Questionnaire(FoP-Q-SF)[J]. Z Psychosom Med Psychother, 2006, 52(3):274-288. |
| [14] | 吴奇云, 叶志霞, 李丽, 等. 癌症患者恐惧疾病进展简化量表的汉化及信效度分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015, 50(12):1515-1519. |
| Wu QY, Ye ZX, Li L, et al. Reliability and validity of Chinese version of Fear of Progression Questionnaire-Short Form for cancer patients[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2015, 50(12):1515-1519. | |
| [15] |
Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress[J]. J Health Soc Behav, 1983, 24(4):385-396.
PMID |
| [16] | 杨廷忠, 黄汉腾. 社会转型中城市居民心理压力的流行病学研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2003, 23(9):11-15. |
| Yang TZ, Huang HT. An epidemiological study on stress among urban residents in social transition period[J]. Chin J Epidem, 2003, 23(9):11-15. | |
| [17] | 肖水源. 《社会支持评定量表》的理论基础与研究应用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志, 1994, 4(2):98-100. |
| Xiao SY. The theoretical basis and research application of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Clin Psychol Med, 1994, 4(2):98-100. | |
| [18] | 刘继文, 李富业, 连玉龙. 社会支持评定量表的信度效度研究[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2008, 31(1):1-3. |
| Liu JW, Li FY, Lian YL. Reliability and validity of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Xinjiang Med Univ, 2008, 31(1):1-3. | |
| [19] |
Kroemeke A. Changes in well-being after myocardial infarction:does coping matter?[J]. Qual Life Res, 2016, 25(10):2593-2601.
DOI URL |
| [20] | 刘瑾文, 刘鸣雷, 齐艳. 基于症状管理理论的冠心病病人恐惧疾病进展危险因素分析[J]. 护理研究, 2022, 36(10):1771-1778. |
| Liu JW, Liu ML, Qi Y, et al. Risk factors of fear of progression in patients with coronary heart disease based on symptom management theory[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2022, 36(10):1771-1778. | |
| [21] |
Koch-Gallenkamp L, Bertram H, Eberle A, et al. Fear of recurrence in long-term cancer survivors-Do cancer type,sex,time since diagnosis,and social support matter?[J]. Health Psychol, 2016, 35(12):1329-1333.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | 杜若飞, 陈长英. 心肌梗死患者重返工作岗位后心理体验的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(8):920-925. |
| Du RF, Chen CY. A qualitative study on psychological experience of patients with myocardial infarction after returning to work[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(8):920-925. | |
| [23] |
余红雨, 杨巧红, 李耀霞, 等. 中青年急性心肌梗死患者社会适应体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(9):1387-1393.
DOI |
|
Yu HY, Yang QH, Li YX, et al. The psychosocial adaptation experience of young and middle-aged patients with acute myocardial infarction:a qualitative meta-synthesis[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(9):1387-1393.
DOI |
|
| [24] | 于海霞, 李彦. 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者D型人格与社会支持的相关性研究[J]. 护理学报, 2015, 22(9):76-78. |
| Yu HX, Li Y. Correlation between type D personality and social support in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. J Nurs China, 2015, 22(9):76-78. | |
| [25] |
郝瑞霞, 李育玲, 徐勇, 等. 冠心病患者负性情绪智能化改善方案的制订及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2021, 56(9):1285-1292.
DOI |
|
Hao RX, Li YL, Xu Y, et al. Study on the development and application effect of an intelligent negative emotion improvement program for patients with coronary heart disease[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2021, 56(9):1285-1292.
DOI |
|
| [26] |
Ozdemir S, Teo I, Bundoc FG, et al. Role in decision making among congestive heart failure patients and its association with patient outcomes:a baseline analysis of the SCOPAH study[J]. Patient Educ Couns, 2021, 104(3):496-504.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 石珂, 张海玲, 钱荣, 赵雯静, 管晓红, 汪澄, 李隽祎. 肾移植患者住院期间体力活动的循证护理实践[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 389-397. |
| [2] | 夏瑶瑶, 李颐, 熊晓云, 周亮, 王艳慧, 马兰英. 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗患者心脏康复信息需求和自我管理的研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 398-405. |
| [3] | 于甜栖, 孙国珍, 高敏, 王洁, 刘沈馨雨, 黄杨曦, 鲍志鹏. 慢性心力衰竭患者运动康复参与护理干预方案的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 414-420. |
| [4] | 陈建静, 谢幸尔, 储红梅, 蔡义红, 曹秋月, 张敏. 老年慢性心力衰竭患者积极运动体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 421-425. |
| [5] | 郭卫婷, 刘建萍, 张晓雪, 张彬彬, 吴煜峥, 王文君. 远程心脏康复有效性及依从性的系统评价再评价[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 426-432. |
| [6] | 周英凤, 黄娜, 李丽, 方园, 邢年路, 赵敏慧, 朱佳蕾, 汪玲. 基于保护动机理论的妊娠期糖尿病孕妇血糖管理决策行为模型的构建[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 433-439. |
| [7] | 蒋琪霞, 刘国帧, 朱玉玲, 李育梅, 展颖颖, 于秀娟, 解怡洁, 王静, 白育瑄. Braden量表诊断老年人压力性损伤的适用性和最佳界值的多中心研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 440-445. |
| [8] | 李欣, 孙超, 胡慧秀, 赵雅洁, 刘晨霞. 养老机构老年人认知功能现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 446-451. |
| [9] | 田君叶, 吴欣娟, 路潜, 郭爱敏, 王艳玲, 张霞, 丁炎明. 专科护士同质化培训管理方案的构建与应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 452-458. |
| [10] | 胡欣欣, 丁玥, 邓玉华, 方蘅英, 潘英华. 1例贝赫切特综合征患儿行心脏瓣膜置换术后并发脑卒中的护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 459-462. |
| [11] | 王钰, 陈佳茵, 刘宁. 系统性红斑狼疮患者生育期保健的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 463-470. |
| [12] | 江鸿展, 陈丽娟, 申嘉丽, 林慧慧. 老年患者失禁相关性皮炎危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 471-476. |
| [13] | 徐欣怡, 唐莉, 余雅婷, 陈晓容, 毛孝容, 闵丽华. 学龄期恶性肿瘤患儿运动康复的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 477-484. |
| [14] | 张泽涵, 苗波, 闫晓霞, 仇雪娟, 巩毅娟, 张爱枝. 脑死亡患者家属器官捐献决策体验的Meta整合[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 485-492. |
| [15] | 孟令琦, 刘佳惠, 彭思意, 魏涛, 李星凤, 林琴, 马航霞, 戚熠, 李旭英. 创伤患者静脉血栓栓塞症风险预测模型的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2023, 58(4): 493-498. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||