


中华护理杂志 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (1): 36-41.DOI: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.01.005
王晶晶( ), 白晨晓, 张泽懿, 伊默, 贾元敏, 陈欧(
), 白晨晓, 张泽懿, 伊默, 贾元敏, 陈欧( )
)
收稿日期:2021-06-01
出版日期:2022-01-10
发布日期:2022-01-11
通讯作者:
陈欧,E-mail: chenou@sdu.edu.cn作者简介:王晶晶:女,本科 (硕士在读),E-mail: wjj17803862611@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Jingjing( ), BAI Chenxiao, ZHANG Zeyi, YI Mo, JIA Yuanmin, CHEN Ou(
), BAI Chenxiao, ZHANG Zeyi, YI Mo, JIA Yuanmin, CHEN Ou( )
)
Received:2021-06-01
Online:2022-01-10
Published:2022-01-11
摘要:
目的 评估老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病 (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,COPD) 患者锻炼行为感知水平,并分析其影响因素。方法 采用方便抽样法,选取2018年12月—2019年6月于济南市4所三级甲等医院住院的207例老年COPD患者作为调查对象。采用一般资料调查表、锻炼益处及障碍量表、呼吸困难信念问卷、COPD患者自我效能量表和社会支持评定量表进行调查。 结果 207例老年COPD患者锻炼益处及障碍量表得分为 (127.34±11.71) 分,锻炼行为感知与恐惧活动信念呈负相关 (r=-0.469,P<0.001),与自我效能和社会支持均呈正相关 (r=0.412,P<0.001;r=0.247,P<0.001) 。多元线性回归分析结果显示,恐惧活动信念、自我效能、社会支持及患病前体力活动情况是锻炼行为感知的影响因素。 结论 老年COPD患者的锻炼行为感知水平有待提高。加强对COPD患者及其家属的运动康复教育和指导,帮助患者消除或降低对体力活动的恐惧,提高自我效能感和获取、利用社会支持的能力,有利于改善其对锻炼行为的感知。
王晶晶, 白晨晓, 张泽懿, 伊默, 贾元敏, 陈欧. 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者锻炼行为感知现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 36-41.
WANG Jingjing, BAI Chenxiao, ZHANG Zeyi, YI Mo, JIA Yuanmin, CHEN Ou. The current status of exercise perception and its influencing factors in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Nursing, 2022, 57(1): 36-41.
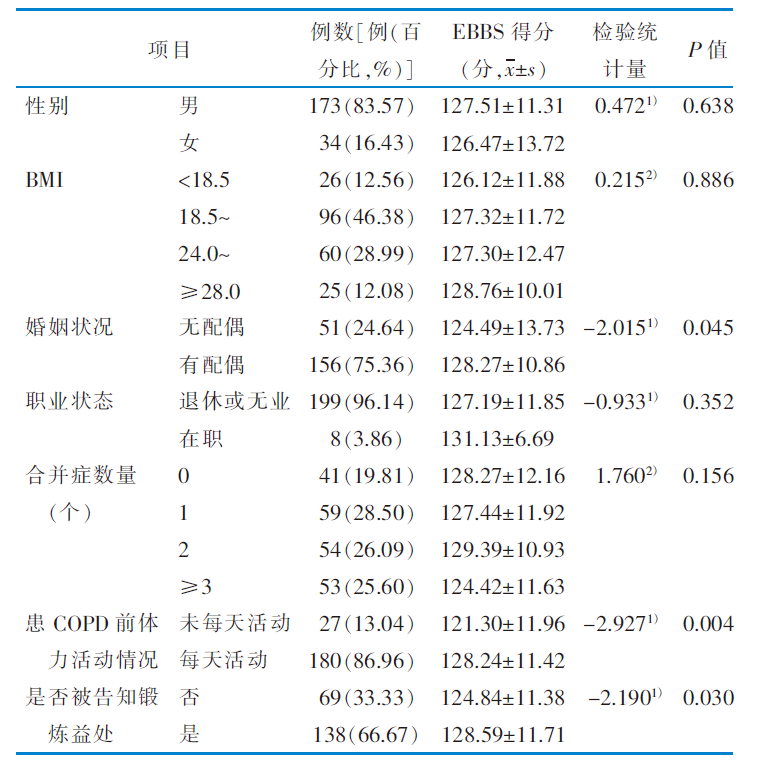 |
表1 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者的一般资料及锻炼行为感知影响因素的单因素分析结果 (n=207)
Table 1 The general data of subjects and univariate analysis of exercise perception for elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (n=207)
 |
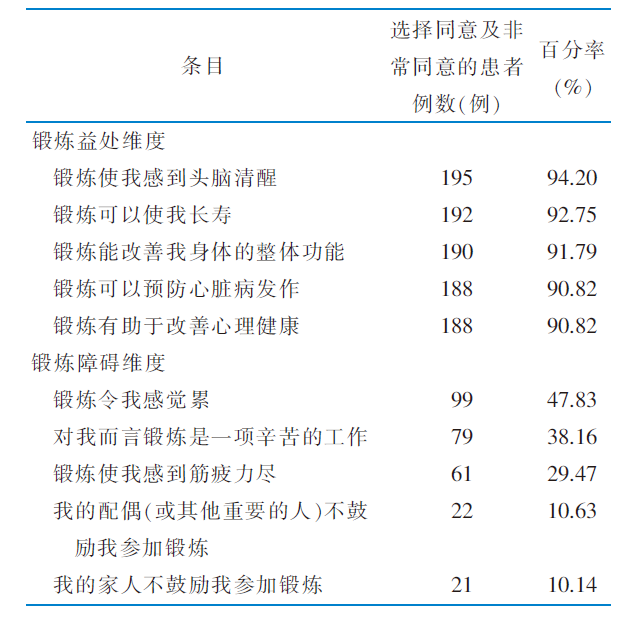 |
表2 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者在锻炼益处和锻炼障碍维度中选择同意及非常同意的比例位于前5位的条目 (n=207)
Table 2 The five items with the highest proportion of agree and strongly agree were selected for exercise benefits dimension and exercise barriers dimension in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (n=207)
 |
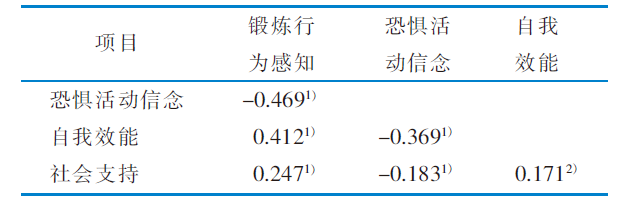 |
表3 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者锻炼行为感知、恐惧活动信念、自我效能、社会支持的相关性分析结果 (n=207,r 值)
Table 3 Correlation analysis of exercise perception,activity-related fear,self-efficacy and social support in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (n=207, r value)
 |
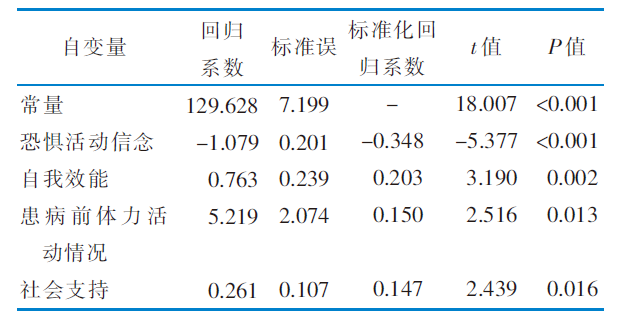 |
表5 老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者锻炼行为感知影响因素的多元线性回归分析结果 (n=207)
Table 5 Results of multiple linear regression analysis of factors influencing exercise perception in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (n=207)
 |
| [1] | Wang C, Xu JY, Yang L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China(the China Pulmonary Health[CPH] study):a national cross-sectional study[J]. Lan-cet, 2018, 391(10131):1706-1717. |
| [2] | World Health Organization. Physical activity[EB/OL].(2020-11-26)[2020-12-25]. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity. |
| [3] |
Fuertes E, Carsin AE, Antó JM, et al. Leisure-time vigorous physical activity is associated with better lung function:the prospective ECRHS study[J]. Thorax, 2018, 73(4):376-384.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Demeyer H, Costilla-Frias M, Louvaris Z, et al. Both moderate and severe exacerbations accelerate physical activity decline in COPD patients[J]. Eur Respir J, 2018, 51(1):1702110.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Sievi NA, Brack T, Brutsche MH, et al. Physical activity declines in COPD while exercise capacity remains stable:a longitudinal study over 5 years[J]. Respir Med, 2018, 141:1-6.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Pender NJ, Walker SN, Sechrist KR, et al. Development and testing of the health promotion model[J]. Cardiovasc Nurs, 1988, 24(6):41-43.
PMID |
| [7] | Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis,management and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 2018 report[EB/OL]. (2017-11-15)[2020-12-25]. http://www.goldcoped.org. |
| [8] | 中华医学会呼吸病学分会慢性阻塞性肺疾病学组. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病诊治指南(2013年修订版)[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2014, 6(2):67-80. |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Group, Respiratory Branch, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(2013 revision)[J]. Chin J Frontiers of Med(Electronic Edition), 2014, 6(2):67-80. | |
| [9] |
Sechrist KR, Walker SN, Pender NJ. Development and psychometric evaluation of the Exercise Benefits/Barriers Scale[J]. Res Nurs Health, 1987, 10(6):357-365.
PMID |
| [10] | 郑晶. 维持性血液透析患者体力活动及其影响因素[D]. 广州:中山大学, 2009. |
| Zheng J. Physical activity and correlation in maintenance hemodialysis patients[D]. Guangzhou:Sun Yat-sen University, 2009. | |
| [11] |
De Peuter S, Janssens T, van Diest I, et al. Dyspnea-related anxiety:the Dutch version of the Breathlessness Beliefs Questionnaire[J]. Chron Respir Dis, 2011, 8(1):11-19.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 伍青. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者呼吸困难信念及其对功能状态影响的研究[D]. 北京:中国医学科学院北京协和医学院, 2015. |
| Wu Q. Breathlessness beliefs and its effect on functional status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[D]. Beijing:Peking Union Medical University,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, 2015. | |
| [13] |
Wong KW, Wong FK, Chan MF. Effects of nurse-initiated telephone follow-up on self-efficacy among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. J Adv Nurs, 2005, 49(2):210-222.
DOI URL |
| [14] | 肖水源. 《社会支持评定量表》的理论基础与研究应用[J]. 临床精神医学杂志, 1994, 4(2):98-100. |
| Xiao SY. The theoretical basis and research application of Social Support Rating Scale[J]. J Clin Psychol Med, 1994, 4(2):98-100. | |
| [15] | 杨凡, 潘越, 邹泽宇. 中国老年人体育锻炼状况及影响因素研究[J]. 中国体育科技, 2019, 55(10):10-21,40. |
| Yang F, Pan Y, Zou ZY. Patterns and determinants of physical activity of elderly people in China[J]. China Sport Sci Technol, 2019, 55(10):10-21,40. | |
| [16] | 张利峰, 张美芬, 肖萍, 等. 老年全髋关节置换术后患者的康复锻炼自我效能及其相关因素的研究[J]. 护理管理杂志, 2017, 17(10):717-719. |
| Zhang LF, Zhang MF, Xiao P, et al. Study on self-efficacy and related factors of rehabilitation exercise in elderly patients after total hip replacement[J]. J Nurs Adm, 2017, 17(10):717-719. | |
| [17] |
Matson TE, Anderson ML, Renz AD, et al. Changes in self-reported health and psychosocial outcomes in older adults enrolled in sedentary behavior intervention study[J]. Am J Health Promot, 2019, 33(7):1053-1057.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Wang HC, Tsai JC, Chao YF, et al. An exploration of beliefs regarding exercise among Taiwanese patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Heart Lung, 2013, 42(2):133-138.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
罗媛容, 陈妙霞, 吴少珠, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者日常体力活动影响因素的质性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(21):2635-2641.
DOI |
| Luo YR, Chen MX, Wu SZ, et al. Daily physical activity in patients living with COPD:a qualitative study[J]. Chin Gen Pract, 2020, 23(21):2635-2641. | |
| [20] | 王秀秀, 蒋玉宇, 王姗姗, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者肺康复体验的质性研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(5):696-702. |
| Wang XX, Jiang YY, Wang SS, et al. A qualitative study on coping strategies of pulmonary rehabilitation barriers in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(5):696-702. | |
| [21] | 朱建俊, 陆洪国, 胡志伟, 等. 呼吸困难信念对老年慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者功能状态的影响[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2017, 25(6):453-456. |
| Zhu JJ, Lu HG, Hu ZW, et al. Effect of breathlessness beliefs on functional status in elderly patients with COPD[J]. Chin J Prev Control Chronic Dis, 2017, 25(6):453-456. | |
| [22] |
Hoaas H, Andreassen HK, Lien LA, et al. Adherence and factors affecting satisfaction in long-term telerehabilitation for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:a mixed methods study[J]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2016, 16:26.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
DePew ZS, Garofoli AC, Novotny PJ, et al. Screening for severe physical inactivity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:the value of simple measures and the validation of two physical activity questionnaires[J]. Chron Respir Dis, 2013, 10(1):19-27.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Darawad MW, Khalil AA, Hamdan-Mansour AM, et al. Perceived exercise self-efficacy,benefits and barriers,and commitment to a plan for exercise among Jordanians with chronic illnesses[J]. Rehabil Nurs, 2016, 41(6):342-351.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Meshe OF, Bungay H, Claydon LS. Participants’ experiences of the benefits,barriers and facilitators of attending a community-based exercise programme for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Health Soc Care Community, 2020, 28(3):969-978.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Dinges NG, Joos SK. Stress,coping,and health:models of interaction for Indian and native populations[J]. Am Indian Alsk Native Ment Health Res Monogr Ser, 1988, 1:8-64.
PMID |
| [27] | 张义静, 李娟, 孙丽, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者早期简易肺康复方案的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2020, 55(5):690-695. |
| Zhang YJ, Li J, Sun L, et al. Construction of an early simple pulmonary rehabilitation programme for patients with COPD and its evaluation of effectiveness[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2020, 55(5):690-695. | |
| [28] | 郭燕红. 实施健康中国战略推动护理事业发展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018, 53(1):5. |
| Guo YH. Implementing Healthy China strategy and promoting nursing development[J]. Chin J Nurs, 2018, 53(1):5. |
| [1] | 赵春娜, 黄永望, 潘静, 傅德慧, 赵京, 庄丕伟, 尤海燕, 于金宝, 李恺玥. 四部矫治康复训练在声带良性病变手术患者中的应用研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 10-16. |
| [2] | 麦秋露, 王君鑫, 杨丹, 李学靖, 张小艳, 郝玉芳. 我国临床护理实践指南改编研究的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 105-112. |
| [3] | 张雯杰, 葛娟, 韩玉琴, 黎瑞红. 糖尿病患者医疗机构外锐器废物处置现状的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 113-117. |
| [4] | 陈海丽, 肖志田, 叶敬花, 田小琴. 癫痫患者从青少年到成人过渡期护理的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 118-123. |
| [5] | 许敬华, 徐海东, 唐敏, 梁婧, 李啸扬, 王濬, 朱大乔, 景峰. 输液滴速计数器的设计与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 124-128. |
| [6] | 李逗逗, 姚瑶, 曹琳, 郑仁东, 何志伟, 姚平, 王雅琳, 孙宇, 朱登月, 刘超. 专科护士主导的2型糖尿病患者共享门诊的构建及应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 17-22. |
| [7] | 柳蕊, 周春兰, 刘宇霞, 章明阳, 张银英, 聂芳. 4种平衡功能测试方法在慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者中应用的比较[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 23-28. |
| [8] | 蔡梦骞, 崔妙玲, 农荧, 覃金莲, 莫素猜, 杨珍娇. 稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者报告结局现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 29-35. |
| [9] | 张晓娜, 李鑫丹, 芦鸿雁, 赵杰, 冯向侃. 出院准备服务对慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 42-48. |
| [10] | 杨雪凝, 李雪儿, 王松, 方紫妍, 柳静, Akimana Sandra, 张静. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者呼吸肌训练的最佳证据总结[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 49-55. |
| [11] | 肖丹, 郭婷, 涂惠, 李欣, 刘佳文, 陈华, 魏雯婷, 易凤仪, 熊晓云. 桡动脉压迫期间血压波动对经皮冠状动脉介入治疗后患者术侧手掌肿胀的影响[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 56-60. |
| [12] | 向洋, 倪崴莲. 气管插管非计划性拔管预警及决策支持系统的研发与应用[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 61-65. |
| [13] | 杨娟, 李牧玲, 李春梅, 黄清辉, 林少钦, 周宏珍. 眼科住院患者跌倒风险评估量表的构建及初步验证[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 66-72. |
| [14] | 林韦彤, 刘立芳, 万晶晶, 刘晶晶, 杨梦, 马航霞. 肾移植受者恐惧疾病进展现状及影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 73-78. |
| [15] | 王芳, 卢芳燕, 王燕. 6例经典型枫糖尿病患儿行肝移植的术后护理[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(1): 79-82. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||